1º trimestre
HUMAN BEINGS AND HEALTH
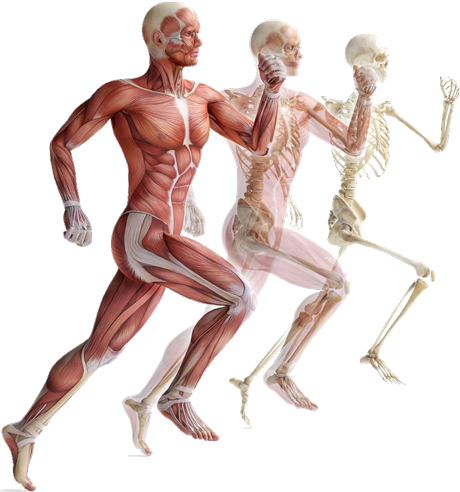
2.- NERVE CELLS
Here you have some videos to remember important facts about them:
OUR SENSES

What's your favourite flavour icecream?
Check your knowledge about this section in the following links:
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/4843425-unit_1_interaction.html
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/2647747-the_nervous_system_3_brain.html
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/4930926-our_senses.html
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/4801403-locate_the_five_senses.html
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/2647017-the_sensory_system_1.html
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/2647025-the_sensory_system_2.html
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/4541367-can_you_find_all_the_senses.html
•Function: to support and give shape to our body;toprotect our internal
organs.•It is made up of bones (hard bone tissue) andcartilage (flexible tissue).•Types of bones:
-Short and wide (vertebrae): support andstability.-Flat and thin (ribs): protect our internal organs.-Long and strong (arms and legs bones):movement.
•Ligaments (strong, elastic tissue) connect bonesat the joints.•Types of joints:
-Fixed joints: join bones in our skull. Nomovement.-Semi-flexible joints: vertebrae in our spine. Somemovement.-Flexible joints: Neck, shoulders (the mostflexible), elbows, wrists,
knees, ankles and waist. Alot of movement.
•Function: Muscles give our body shape andrespond to the nervous system
contracting andrelaxing.•Tendons (tissues) connect muscles to bones.•Types of muscles:
-voluntary: we can move them at will (the musclesin our arms).-involuntary: muscles move automatically (the muscles in our heart)
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/4097372-mapa_interactivo.html
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/4071884-musculoskeetal_system.html
VIDEOS
muscles and bones.
Time to check what you remember!
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/4097372-mapa_interactivo.html
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/4071884-musculoskeetal_system.html
b_ NUTRITION
The process seems simple but it is really special.
WHy don't we do a little review in Spanish to understand the whole process a bit more?
Summary body systems
Summary 1
Summary 3
The excretory system
Let's see some videos about it:
Why is healthy food important?
Let's have some fun reviewing your knowledge on this section!
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/3803591-nutrition.html
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/2646901-the_digestive_system.html
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/2646918-the_respiratory_system.html
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/3803676-the_circulatory_system.html
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/2646931-the_circulatory_and_the_excretory_systems.html
https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/2884454-listen_excretory_system_bilingue.html
The Digestive System
The Respiratory System:
The Circulatory System:
How your heart works:
Th Excretory System:
The Urinary System:
Sweat glands:
SPAIN AND EUROPE
Hello, Spaniards! We live in a wonderful country, divided in 17 Autonomous Communities and 2 Autonomous Cities. Some of them are also divided in different provinces. Do you remember all of them?
Test your knowledge in the following links:
http://serbal.pntic.mec.es/ealg0027/mapasflash.htm
https://mapasinteractivos.didactalia.net/comunidad/mapasflashinteractivos/recurso/rios-de-espaa/6b90cb5d-8084-4d44-9cc6-990fe7068e38
https://mapasinteractivos.didactalia.net/comunidad/mapasflashinteractivos/recurso/relieve-de-espaa/b08c36e5-ed54-46e1-995f-354b59d8dd08
Finally, you will find useful information about Spain in the following Prezi presentations:
https://prezi.com/y1sjt6bwot89/t1-geografia-de-espana-6o-primaria/
Vídeos
https://prezi.com/m/y1sjt6bwot89/t1-geografia-de-espana-6o-primaria/
https://prezi.com/m/d5wg3u4svo09/la-geografia-de-espana/

Vídeo
El relieve de España: Mapa interactivo para repasar
La hidrografía de España: Mapa interactivo para repasar.
La canción de los ríos:
ESPAÑA
WE ARE PART OF EUROPE!
Spain is only one of the many countries which can be found in our continent, Europe. We are sure you can name a lot more and their capitals! Do you want to check? Click here:
- Capitals
- River
- Videos
Unidad EUROPA
Finally, we were interested in the flags of the different countries... here you can have a look at European flags! Then, click the link to check if you recognise them.
https://online.seterra.com/es/fl/2011
LET'S PLAY!
We learnt in class different landmarks that we can find all over Europe... Do you want to test yourself?
https://create.kahoot.it/share/enter-kahoot-title/8502ce7f-1a1e-4582-b87f-ac2b1d1ae362
Remember! To play this Kahoot, you will need another device (mobile phone, tablet...).

Summary 18-19 th century
We live in the Modern Age, a period which started in 1789 with the FrenchRevolution and continues to the present day.
- King: Louis XVI-->MONARCHY : ABSOLUTE POWER
- France was in crisis
- Social inequalities: Extremely poor people
- 14 July (1789):Attack to the Bastille prisión
- NAPOLEON: militar y Commander/ Emperor of France
- Empiece with Europeas contries
- Conquer Portugal crossing Spain
1 Poder: legislativo, executive and judicial
- Monarchy was abolished
- 1793 Louis XVI-- was killer
- REPUBLIC:
- Ideas: Liberty, equality and fraternity
- King: Carlos IV
- Prime minister =>Godoy
- Treaty of Fontainebleau (1807)
- NAPOLEON conquered Spain
- In 1808: Napoleón Bonaparte, the Emperor of France, invaded Spain.
- On 2nd May, 1808, an uprising in Madrid led to the War of Independence against France. Under Napoleon Bonaparte (the Emperor of France), the French army had occupied Spain. REVOLUCION
 During : 2 goverments
During : 2 govermentsMadridNapoleon's brother, Joseph Bonaparte, became kingFrench controlled most of SpainCádizHeaded by Fernando Vii ( Carlos IV's son)CONSTITUCION OF CÁDIZ 1812= liberal:1 king's poder was reduces2Power legislativo, executive and judicial3 Vote( men)4 Press= Freedom
- Spain won
- The King Ferdinand VII was forced to abdicate.
- No constitución of Cádiz
- ABSOLUTE MONARCHY
- The Spanish parliament, or Cortes, took refuge in Cadiz. In 1812 they wrote the firsmodern Constitution, the Constitution of Cadiz (La Pepa).
- It limited the king's power.
- It stablished the right of citizens, including the vote for 25 year-old men.
- In 1814 Ferdinand VII was restored as King. Initially, he did not accept the Constitution and he ruled in an authoritarian manner.
- In 1820 Ferdinand VII was forced to accept the Constitution after the revolt. Three years later he was restored as an absolute monarch with the help of the French.
- The political chaos in Spain caused an independence movement in the Spanish colonies in Spain.
- In 1824 all the American colonies except Cuba and Puerto Rico were independent.
Before
- Fernando VII was the King
- FernandoVII oo María Cristina =>Isabel II
- FernandoVII chances the low => renales could inhent the throne
- Fernando diez
- Carlos ( Fernando's brother) wonted the throne
During
Liberals
Carlists
- Supported Carlos
- No chances
- ABSOLUTE MONARCHY
- Catholic church
- 2 more Wars
- Liberal victory
- Central America
- south America
- Colonists wanted --> Frreedom
-- > Ls influenced by the FRENCH REVOLUTION
- Spain = war of INDEPENDENCE against French. --> its control was weaker
What is it?--> Economic and technological charges.
when and where did it start?: It began in GREAT BRITAIN in the 18th centun
Inventions: stem engine products could be made in Factores
when did it start in Spain?: During the 19th century
--àwhy? - Spain's economy was bound in AGRICULTURE
Transports:
o powered by coal.
o Railway network expanded
o It was easier to transport à Products
à People
SOCIETY
Before = ESTATESà CLERGY
à NOBILITY
à ORDINARY PEOPLE ( TAXES /No prIVILEG)
After= CLASSESà UPPER (Rich factory owners/ bankers)
à MIDDLE = Bourgeoisie:
è Civil servants
è Lawyers
è Doctors
è small landowners
à working class= proletariat
- The First Republic
- Amadeo of Savoy (1st Amadeo of Savoy; 2nd The First Republic, 3rd Alfonso XII)
- Alfonso XII
Throughout his extensive career, the painter will touch on all kinds of subjects using different techniques, although he is an artist who does not have a clear technical evolution.
- The first one covers from 1771 to 1807, it is the time of youth and maturity, that of professional triumphs, in which the optimistic vision of life predominates. He started here as an Academy and Royal painter, painting members of the Court and the most select members of the Spanish nobility. He also paints the cartoons for the Royal Tapestry Factory. In 1792 he became seriously ill and although he overcame the illness, it left him with severe deafness that caused him to gradually isolate himself, entering his internal world, letting out a new Goya.
El Aquelarre (1798)

El sueño de la razón produce monstruos (1799)

La maja desnuda (1800)
La maja vestida (1800 – 1808)

- The second stage covers the years 1808-24 approximately. These are the years marked by deafness and war. He rents a house, the "Quinta del sordo", a place where he makes "Black Paintings" on its walls, with a dramatic and gloomy theme, the result of his pessimism, with a dark palette, in which black predominates and with a dense brushwork, almost material, even using the spatula to apply the paste, in which the drawing has been broken, since it is a painting of stains.
El Coloso (1808 – 1812)
El fusilamiento del 3 de mayo (1808 – 1812)
Autorretrato (1815)
Duelo a garrotazos (1819 – 1823)
Saturno devorando a su hijo (1819 – 1823)
Dos viejos comiendo sopa (1819 – 1823)
Ficheros adicionales
Finally, here you have a summarising video from Teacher Ms. Isabel, from the French Revolution to the Bourbon Restoration... Enjoy the trip to our past!
And remember, knowing the past allows us to understand the present and improve the future.
LOS INICIOS DE LA EDAD CONTEMPORÁNEA EN ESPAÑA
EDAD CONTEMPORÁNEA SIGLO XIX (hasta el 13.30, lo que sigue corresponde al tema 4)
ARTE Y CULTURA EN ESPAÑA. SIGLO XIX.
LA FAMILIA DE CARLOS IV - GOYA (EL MUSEO DEL PRADO)
- 1789 French Revolution
- 14 July 1789 Bastille
- 1793 King Louis XVI--killer
- 1804 Napoleón Emperador of France
- 2 May 1808 guerrilla War
- 1812 Constitution of Cádiz
- 1814 end of spanish War of Independencience
- 1810/ 1825 spain's colonias in America
- 1833 FernandoVII died=> Carlist Wars
- 1833/1868 the reign of Isabel II
- 1839 liberal victory
- 1868 abdicated
- 1871 Amadeo of Savoy
- 1873 Fist Republic
- 1874 Restoration
- 1898 Spanish-american war
c._ REPRODUCTION
Summary unit
Male Reproductive System

- the testicles
- the duct system, which is made up of the epididymis and the vas deferens
- the accessory glands, which include the seminal vesicles and prostate gland
- the penis
- Testes: The two testes (one of them is called a testis) are contained in a bag of skin called the scrotum. They have two functions:
- to produce millions of male sex cells called sperm
- to make male sex hormones, which affect the way a man's body develops.
- Sperm duct and glands The sperm pass through the sperm ducts, and mix with fluids produced by the glands. The fluids provide the sperm cells with nutrients. The mixture of sperm and fluids is called semen.
- Penis and urethra : The penis has two functions:
- to pass urine out of the man's body
- to pass semen into the vagina of a woman during sexual intercourse.The urethra is the tube inside the penis that can carry urine or semen. A ring of muscle makes sure that there is no chance of urine and semen getting mixed up.


FICHA




GAMETE

HUMAN REPRODUCTION

The miracle of life
Like other living things, human beings reproduce. It's what keeps the population going. In humans, the male and female reproductive systems work together to make a baby.
Fertilisation
During sexual intercourse the man's penis releases semen into the woman's vagina. Sperm cells travel in semen from the penis and into the top of the vagina. They enter the uterus through the cervix and travel to the egg tubes. If a sperm cell meets with an egg cell there, fertilisation can happen. Fertilisation happens when an egg cell meets with a sperm cell and joins with it.
The fertilised egg divides to form a ball of cells called an embryo. This attaches to the lining of the uterus and begins to develop into a foetus (pronounced "fee-tuss") and finally a baby.
Reproduction

EXAM 1
EXAM 2
Moderno Spain: The 20th century
Timeline




- The Monarchy was abolished and the Church lost power.
- The Liberals and Conservatives took turns in government.
- All men and women could vote in elections.
- There was a dictatorship and political parties were illegal.
- There was a new constitution.
- Freedom of the press was limited by censorship.
SUMMARY
CIVIL WAR (1936-1939)
Video clan democracia
 |
| Leopoldo Calvo Sotelo was chosen to succeed Adolfo Suarez. |



Resumen
ARTISTIC MOVEMENTS IN THE 19TH AND 20TH CENTURY




Resumen 1
Resumen 2
Visitas virtuales
Unit 5
ORGANIZATION
- Check this interactive diagram to find out more about the E.U. Institutions
- On this link, you can click on the European countries so you can learn their names.
- And here, you can play different games to check how many European countries you know (Easy - medium - hard)
- One more game for you to learn the European countries!
- Do you know all the countries that make up the E.U.? Let's check it out!!!
- It is time to learn the capitals in Europe...
- Which E.U. countries use the EURO as their currency?
- This presentation will allow you to know more about the European Institutions.
- This is the link to the France glogster so you can see what you will have to do...












































































































































































































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario