HELLO EVERYONE
AND
WELCOME TO THE BLOG!
1st Term
UNIT 1: HUMAN BEINGS AND HEALTH
LET'S LEARN ABOUT THE HUMAN BODY...


The circulatory system moves blood around our body. That is what we call blood circulation.
Our blood has 2 main FUNCTIONS:
- It transports nutrients and oxygen to the different parts of our body.
- It collects waste substances (the substances our body doesn't need).

Blood travels around our body through blood vessels.
There are 3 different types of blood vessels:
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the rest of the body. They carry oxygenated blood (blood with oxygen) that is bright red.
- Veins carry blood back to the heart from the rest of the body. They carry deoxygenated blood (blood with carbon dioxide) that is dark red.








Ficha interactiva 1
Ficha interactiva 2
Summary
Summary
Let's have some fun reviewing your knowledge on this section:
- The digestive system_Sopa de letras
- The digestive system_Match English & Spanish
- The excretory system_Matching game
- The excretory system_Unscramble and write the parts
- https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/7085115-the_excretory_system_n_1.html
- https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/7085218-the_excretory_system_n_2.html
- https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/7085308-the_excretory_system_n_3.html
- https://es.educaplay.com/recursos-educativos/7085374-the_excretory_system_n_4.html
- The digestive and excretory system_Crossword
- The circulatory system_Matching game
- Interactive human body_Body systems mixed
- Body systems_Matching game
INTERACTION
As we learnt in class, we interact with each other and the world since we are born and in many ways. But... what do we need to interact? Exactly! Our nervous system, the five senses and the locomotor system.
Here you have some videos to remember important facts about them:
Check your knowledge about this section in the following links:
REPRODUCTION
It's turn for the third vital function to be learnt: reproduction.
Like many other living things, human beings reproduce by sexual reproduction... What does it mean? We need female and male reproductive cells to reproduce.
REPRODUCTORY SYSTEM



Click here to watch the full video
Time to check all that we know!
Human Body Systems
JUEGO 1
JUEGO 2
Phew! We learnt sooo many things about ourselves in this unit. Now you can understand why we can talk with our friends, ride a bike without falling, watch films and enjoy our meals, do sports, grow, sweat... and the most important, feel happy and express it!
HEALTH AND COMMON ILLNESSES
Remember that in order to keep your nervous system and body healthy, there are some habits we must have!
HEALTHY EATING
We are what we eat! Therefore, our diets need to be healthy and balanced, which means eating a variety of foods with lots of different nutrients.
Do you remember the name of the 4 food groups we have studied?

Minerals and vitamins, carbohydrates, proteins and fats
A HEALTHY LIFESTYLE
We can do other things to keep us healthy, like:

Time to play! Click on the link below to discover a lot of funny games related to healthy habits.
Activities
Contents
Unit 2
PREHISTORY
There are many cave paintings in the Altamira cave in Cantabria. Also, archaeologists have found human bones that are more than 300 000 years old in the Sierra de Atapuerca in Burgos.

Altamira Cave (Cantabria)

Archaeologists working in the excavations of Sierra de Atapuerca (Burgos)
In our country, we can find remains of this period in the cave paintings in El Cogul (Cataluña).
Cave paintings in Roca de los Moros (El cogul, Cataluña)

TIME TO PLAY
Pasatiempos prehistóricos [Necesitáis habilitar Adobe para que funcione]
Prehistory Periods_Complete the interactive mindmap [Educaplay]
Prehistory Periods_Crossword [Educaplay]
Prehistory Periods_Pasapalabra [Educaplay]
Cave paintings_Memory Game [Educaplay]
Prehistory Vocabulary_Word search [Educaplay]
-- o --
HANDS ON! WE ARE PREHISTORIC ARTISTS
Can you imagine going into a cave and discovering how prehistoric people did their paintings? Watch the following 360º video and get immersed in their culture! Also, you can explore around the scene if you click/tap different parts of the window. Enjoy!
Now it's time that you feel like a prehistoric artist! You will only need a brown piece of paper and chalks or finger painting. If you do it, we would be happy if you show us your creation in class!
-- o --
FINALLY... TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE!
CLICK HERE TO PLAY THE REVIEW GAME [GENIALLY]
PREHISTORY: PALEOLITHIC
PREHISTORY: NEOLITHIC
What happened before History? Humans Origins video
- Long Summary Unit 5
- Short Summary Unit 5
- Resumen Unidad 5 Español
- Poster (Timeline: Periods of History)
- Poster (Pre-Roman Spain)
- How do you study History? (video)
- History of the Earth (video)
- Travel through time (video)
- First hominids on Earth and their remains
- Evolution of life before Man to Stone Age (video)
- Life in Prehistoric Times (game)
- Prehistory (Part 1) (video)
- Prehistory (Part 2) (video)
- Prehistory (Part 3) (video)
- Prehistory Learning Guide
- Palaeolithic I (video included in Prezi)
- Palaeolithic II
- Palaeolithic III (video)
- Ancient Art of the Altamira Cave
- From Palaeolithic to Neolithic (video)
- From Palaeolithic to Neolithic Art (video)
- Neolithic (video included in Prezi)
- Metal Ages (video included in Prezi)
- Use of metals (video)
- The Bronze Age I (video)
- The Bronze Age II (video)
- Game where students will learn how to survive in the Iron Age period by collecting the right object in order to make fire or bake bread.
- The history of civilization (video)

2nd TERM.
All living things carry out the three life processes but in different ways... do you remember their names? That's right: nutrition, interaction and reproduction.
To make the study of living things easier we divide them into kingdoms: the Animal, Plant and Fungi Kingdom. Look at the following pictures, can you guess what kingdom do they belong?



1. Plant Kingdom 2. Animal Kingdom 3. Fungi Kingdom


ANIMAL KINGDOM
Have a look at the following presentation of unit 3 made using Prezi:
and at this set of activities to learn, play and review made with Quizlet:
Animals can be classified into vertebrate and invertebrate. Do you remember the difference between them?
VERTEBRATE ANIMALS
All vertebrate animals have a backbone. We can classify vertebrates into five groups: mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish.

INVERTEBRATE ANIMALS
An invertebrate is an animal without a backbone. More than 90% of all living animal species are invertebrates. We can classify them into six groups: mollusks, jellyfish, sponges, echinoderms, annelids/worms and arthropods.
INVERTEBRATES

- Let's watch a video about INVERTEBRATES
- INVERTEBRATES CLASSIFICATION (video included in Prezi)
- ARTHROPODS
- CRUSTACEANS
- MYRIAPODS
- ARACHNIDS
- INSECTS
- MOLLUSCS
- ECHINODERMS (starfish)
- SPONGES
- ANNELIDS
- CNIDARIANS (Coral Reefs)
repasa
- Different GROUPS OF ANIMALS (video)
- Where ANIMALS LIVE (video)
- How ANIMALS GROW AND CHANGE (video)
- AMPHIBIAN, BIRD and MAMMAL RESPIRATORY SYSTEM (video)
- How do FISH BREATH in water? (video)
- BIRDS' BEAKS
- How ANIMALS EAT food (video)
- ANIMAL TEETH facts (video)
- MONOTREMES (video)
- OVOVIVIPAROUS (video)
- REPRODUCTION in animals (video included in Prezi)
- ANIMALS in DANGER
A video about invertebrate animals HERE
MORE GAMES ABOUT ALL TYPES OF ANIMALS HERE AND HERE.
A VIDEO ABOUT VERTEBRATE ANIMALS.... HERE
Plants are different from animals because of two main things... do you remember them? They to do with movement and nutrition... You're right! They can't move around and they make their own food.
We can classify plants in three main groups: grasses, bushes and trees. Looking at the following pictures, match them with their proper definition:

Definition 1: Plants that have a flexible, green stem and are usually short. They grow quickly.
Definition 2: Plants with one big woody stem, called trunk. The branches grow high above the ground. They grow slowly. They are the tallest plants and live the longest.
Definition 3: Plants that have a woody stem but not a trunk. The branches grow near the ground.
Now, watch the following video to learn a bit more about types of plants and their characteristics.
NUTRITION
As you could see briefly in the video, plants produce their own food by photosynthesis. Can you explain it to your parents or a friend? Why is it so important?
Plants are fundamental for the food chain and for our respiration.
REPRODUCTION
Plants reproduce by sexual and/or asexual reproduction. What's the difference between them?
- In sexual reproduction pollen goes from one flower to another.
- In asexual reproduction there are no flowers or fertilisation.
According to this, do you remember the name of the following types of reproduction?

1. Insect pollination 2. Wind pollination 3. Self-pollination 4. Runners 5. Tubers

Now, practice on your plants' knowledge:
Types of plants [LiveWorksheets]
Plants and their life cycle [LiveWorksheets]
at this set of activities to learn, play and review made with Quizlet:
and at this video that summarizes the contents of Unit 4:
Now, have a look at the following links with videos and interesting facts:
- Parts of a PLANT (video)
- ROOTS (video)
- TYPES OF PLANTS (video)
- ADAPTATIONS IN PLANTS (video)
- CARNIVOROUS PLANTS (video)
- DECIDUOUS and EVERGREEN TREES (video)
- PowerPoint Presentation about Photosynthesis
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS (video)
- PLANT NUTRITION and RESPIRATION I (video)
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS and RESPIRATION IN PLANTS II (video)
- Parts of a FLOWER (video)
- Types of REPRODUCTIVE PROCESSES (video)
- Sexual reproduction in FLOWERING PLANTS (video)
- Flowering plants: POLLINATION (video)
- Non-flowering plants: CONES (video)
- How does a SEED become a plant? (video)
- Relations in an ECOSYSTEM (video)
- Impact in the ENVIRONMENT (video)
liveworksheets.com
Aquí os dejo el enlace a la ficha para aquellos que vuestro dispositivo no os deja hacerlo desde el blog.
https://es.liveworksheets.com/jm107840zk
UNIT 4 THE EARTH
PLANET EARTH
Planet Earth is also called 'the blue planet' because it's made up mostly of water. It is the third planet in the Solar System... Do you remember how many planets we can find in it? What are the names?
- we use them to describe a location on the Earth's surface.
- Meridians are vertical lines. Meridian 0º is Greenwich Meridian. Meridians are measured in degrees E or W.
- Parallels are horizontal lines . Parallel 0º is the Equator. Parallels are measured in degrees N or S.
THE EARTH'S MOVEMENTS
The Earth has two different movements: revolution and rotation. Would you be able to explain in which consists each of them?
THE EARTH'S LAYERS
DISCOVERIES
Astronomers study the Sun, Moon, planets and other objects in space.
Thanks to them, we know that the Earth is not flat as they originally believed... what did they find in Ancient History?

You're right, they calculated the Earth was a sphere.
Also, they discovered planets such as Uranus and Neptune using telescopes.
Watch the following videos to learn more about these discoveries:
Here you have some links to practice:
Imaginary Lines_Label the picture [Educaplay]
Imaginary Lines_Matching Activity [Educaplay]
Imaginary Lines_Latitude and Longitude [LiveWorksheets]
Imaginary Lines_Geographic Coordinates Practice [LiveWorksheets]
The Earth's Movements_Choose the correct options [Educaplay]
The Earth's Movements_Fill in the gaps [Educaplay]
The Earth's Movements_ABC Game [Educaplay]
The Earth's Layers_Theory and Practice [LiveWorksheets]
The Earth's Layers_Quiz [Educaplay]
The Earth's Layers_Quiz 2 [Educaplay]
The Earth's Layers_Map Quiz Game [Seterra]
The Earth's Layers_Review Diagram to print [colour]
The Earth's Layers_Review Diagram to print [black and white] You can colour it at home to study!
The Earth_Review whole unit [LiveWorksheets]
PARA SABER MÁS
- PREZI PRESENTATION UNIT 1: EARTH AND SPACE
- (Download Prezi Unit 1 (Earth and Space) offline for Windows)
- Have a look at this video about the SOLAR SYSTEM.
- The BIGGEST STARS in the Universe.
- PLANETS of the SOLAR SYSTEM.
- COMPARISON of the size of the planets HD.
- From the Solar System to our Planet.
- Now it's time to EXPLORE the Solar System.
- FACTS about the Solar System.
- MORE FACTS about the Solar System (powerpoint).
- Why don't you try this QUIZ? (powerpoint).
- Earth's movements (video included in Prezi).
- Why do we have seasons? (video included in Prezi).
- PARALLELS and MERIDIANS (video included in Prezi).
- Latitude and Longitude GAME.
- Why does the Moon change shape?
- PHASES of the Moon.
- Have a look at this VIDEO about the Moon and the Eclipses and find out MORE INFORMATION.
- Famous astronomers (video included in Prezi).
- The HUBBLE TELESCOPE (video included in Prezi).
REVISION MINDMAP.
Will you be able to complete it with the missing words?
![Earth and Geosphere [mindmap]_2.jpg](https://www.educa2.madrid.org/web/educamadrid/principal/files/5ab57864-7f74-4cca-b2de-e766e33cc038/Earth%20and%20Geosphere%20%5Bmindmap%5D_2.jpg?t=1615913142366&largeSize=true)
REMEMBER!
- WEATHER is the atmospheric situation which occurs in a given moment and in a specific place. It can change from day to day.
- We can say the weather is sunny, cloudy, windy...
- CLIMATE is the combination of atmospheric conditions that occur in a place for a prolonged period of time. The elements that make up climate are: temperature, precipitation, humidity, pressure and winds.
- We can say the climate is hot, temperate or cold.
Get to know more about climate here!
CLIMATE ZONES
As we have just learnt, we could say there are three main climate zones on Earth: the Hot or Torrid Zone, the Temperate Zones and the Cold or Frigid Zones.
Watch the following video to review the characteristics of each of them:
Watch this video about the weather
Precipitations
Here you have some links to practice:
Weather_Vocabulary Practice [Wordwall]
Climate_Label the diagram [Wordwall]
Climate_Revision activities [LiveWorksheets]
Weather and Climate_Group Sort Activity [Wordwall]
Weather and Climate_Matching Vocabulary [Wordwall]
Weather and Climate_Vocabulary Review Game [Wordwall]
Weather and Climate_Quiz [Wordwall]
Weather and Climate_Quiz 2 [Wordwall]
Weather and Climate_Quiz 3 [Educaplay]
REVISION MINDMAP. Will you be able to complete it with the missing words?
![Atmosphere, weather and climate [mindmap]_1.jpg](https://www.educa2.madrid.org/web/educamadrid/principal/files/5ab57864-7f74-4cca-b2de-e766e33cc038/Atmosphere%2C%20weather%20and%20climate%20%5Bmindmap%5D_1.jpg?t=1615913287319&largeSize=true)

Weather and climate
THE ATMOSPHERE
LAYERS
The atmosphere is divided into different layers: the troposphere, the stratosphere and the ionosphere.
Can you order the different layers? Look at the picture and label:

1. Troposphere 2. Stratosphere 3. Ionosphere
Now, look at the grey line that crosses the second layer... Do you remember the name? That's right! The Ozone layer!
MÁS MANUALIDADES
- PREZI PRESENTATION UNIT 2: WEATHER AND CLIMATE.
- (Download Prezi Unit 2 (Weather and Climate) offline for Windows)
- Summary about WEATHER.
- Video about WEATHER
- WEATHER INSTRUMENTS (click on "slide show")
- WEATHER INSTRUMENTS (video included in Prezi)
- WEATHER FORECAST (video included in Prezi)
- AIR MASSES AND FRONTS (click on "play videos")
- What is PRECIPITATION? (video)
- Types of PRECIPITATION (video included in Prezi)
- Why does it RAIN? (video)
- What causes THUNDER AND LIGHTNING? (video)
- How is a RAINBOW formed? (video)
- Types of CLOUDS (video included in Prezi)
- Summary about CLIMATE
- WEATHER VS CLIMATE (video)
- How CLIMATE works (video)
- Types of CLIMATE (video included in Prezi)
- Watch this video about the five major types of climates in the world
- More about CLIMATES ZONES OF THE WORLD (video included in Prezi)
- Climates in SPAIN (in English
- Climates in SPAIN (in Spanish)
- Climates in SPAIN (video in Spanish)
THE HYDROSPHERE
WATER BODIES
Do you remember the two types of water that we can find on Earth? What's the difference between them? If you want to refresh your mind, watch the following video!
As you have seen, we can distinguish two main types of water: salt water and fresh water. Now, classify the following water bodies depending on if they are salt water or fresh water.
- Rivers
- Oceans
- Lakes
- Ice caps
- Seas
- Groundwater
(Salt water: oceans and seas; fresh water: rivers, lakes, groundwater and ice caps)
THE WATER CYCLE

The amount of water on Earth never changes. But it does change state... Can you name the three states we know? You're right: solid, liquid and gas.
These different states occur in the constant round of changes known the water cycle.
Videos about the water cycle HERE, HERE AND HERE
The water cycle has four main stages... Unscramble the letters to get their names:
- E r a t i o n v a p o
- s a C o n t i o n d e n
- t i o n t a p i c i P r e
- C o t i o n l l e c
(1. Evaporation 2. Condensation 3. Precipitation 4. Collection)
Let's dance and sing these Water Cycle songs!
GROUNDWATER
Do you want to know more about groundwater and wells? Check these videos out!
RIVERS

REVISION MINDMAP. Will you be able to complete it with the missing words?
![Hydrosphere [mindmap]_3.jpg](https://www.educa2.madrid.org/web/educamadrid/principal/files/5ab57864-7f74-4cca-b2de-e766e33cc038/Hydrosphere%20%5Bmindmap%5D_3.jpg?t=1616021393686&largeSize=true)
Ficheros adicionales
- Section 1_PLANET EARTH [Review questions].pdf
- Section 2_THE ATMOSPHERE [Review questions].pdf
- Section 3_WATER [Review questions].pdf
PARA SABER MÁS
- BODIES OF WATER (video included in Prezi)
- STATES OF WATER (video)
- STATES OF WATER (game)
- Basics of FRESHWATER (video)
- CONTINENTS AND OCEANS labelling game
- Landforms and BODIES of WATER matching game
- The WATER CYCLE (video included in Prezi)
- More about the WATER CYCLE (video)
- EXPERIMENTS with water (video)
- WATER SAVING game
- Locate RIVERS in Spain
- Name RIVERS in Spain
- GROUNDWATER
UNOS POQUITOS CHISTES
¿Qué es el efecto invernadero?






DEL COLE
ROCKS AND MINERALS

Wow, isn't Earth amazing? We have learnt that it has different layers (geosphere, atmosphere and hydrosphere) and we can now say a lot of each of them. Do you remember which is made up of rock?
You're right! The geosphere, specifically the crust, is full of rocks and minerals. Keep reading to know more.
Minerals are substances that are naturally formed in the Earth. They can exist on their own and they can combine with other minerals to make rocks.
Rocks are chunks of minerals, that is, they are made up of one or more minerals. Then, rocks are generally not uniform. There are three main different types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic.
Interesting, isn't it? Watch the following videos for a further explanation and discover the wonders that you can find outside!
Let's go on a tour around the world and discover where people have used rocks and minerals throughout history!
Por si quieres saber más
LITHOSPHERE

1. What 2 sedimentary rocks does he mention?
2. What 2 igneous rocks does he mention?
3. What 2 metamorphic rocks does he mention?
4. What is the most common rock on the surface of the Earth?
New information about minerals:
Remember that the 3 properties of minerals are:
1. Colour
2. Hardness (minerals can be hard or soft)
3. Luster (minerals can be shiny or dull)
Now, watch a video about rocks HERE. What types of rocks do you see during ...
1. minute 2:45 ?
2. minute 3:10 ?
3. minute 3:30 ?
Remember that minerals are useful. We use them for...
Here you have some activities to practise the contepts you know. Write and complete the activities in your notebook.
Interesting sites
- Long Summary Unit 4
- Short Summary Unit 4
- Resumen Unidad 4 Español
- Poster Rock Formation
- Mapa Conceptual Unidad 4
- PREZI PRESENTATION UNIT 4: ROCKS AND MINERALS
- (Download Prezi Unit 4 (Rocks and Minerals) offline for Windows)
- STRUCTURE of the EARTH (video)
- How the EARTH SURFACE has changed (video) .
- Slow and Fast EARTH PROCESSES.
- LAYERS of the Earth (video).
- ROCKS AND MINERALS.
- Types of ROCKS I (video).
- Types of ROCKS II (video).
- Types of ROCKS III (video).
- Types of ROCKS and ROCK CYCLE (video included in Prezi).
- Types of ROCKS and ROCK CYCLE (video)
- Types of ROCKS (song).
- Be a Rock Detective. IDENTIFYING ROCKS (video).
- Identifying Rocks Activity (video)
- Look at different Rocks through a magnifying glass.
- All about VOLCANOES (video).
- What is a VOLCANO? How does it erupt? (video)
- A Brief introduction to MINERALS (video included in Prezi)
- Properties of MINERALS (video).
- What are FOSSILS and how they are formed? (video)
- FOSSILS and ROCK identification (video)
https://miplumier4ccss.wordpress.com/
Everything around us is matter. We can define matter as everything that has weight and takes up space or has volume.
Matter comes in different states... Do you remember the three most common states? You're right: solid, liquid and gas.
STATES OF MATTER
As we have studied, the three most common states of matter are known as solid, liquid and gas. Let's check the following video and anchor chart to refresh our minds about their characteristics!

So... will you classify properly the following things? Check your knowledge on matter states!

Solid: people, bell, crayons, computer, books, soccer ball, pear, hat, ice, flowers.
Liquid: rain, soda, glue, syrup, lemonade, milk, gasoline.
Gas: Sun, helium, rocket exhaust, smoke, steam, hot air, oxygen.
PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
We use wood, metal, plastic, glass and fabric to make most everyday objects, but... do you know how to describe them?
We can also classify materials in thermal insulators and thermal conductors. Can you remember the difference?
- Thermal conductors can get very hot as their molecules are free to move about. Examples: water, glass and metal.
- Thermal insulators can't get hot as their molecules are close together and can't move about. Examples: plastic, fabric and wood.
Here we go again... Will you be able to classify the following materials in conductor or insulator?

MIXTURES AND SOLUTIONS
FORCES
Now that we can define matter and identify materials' properties, let's tack about motion and forces... Have you ever wondered why we can move and walk on our feet, airplanes fly or fish swim?

We can't see forces, but we can feel their effect. For example, forces make things move or stop. They can change the shape of an object or even break it. They make things fall to the ground or stay still. They also make things float or sink.
PUSH AND PULL FORCES


- Balanced forces don't make an object move as the forces applied are opposite and equal.
- Unbalanced forces can make an object start moving, speed up, slow down, change direction or stop.
Look at the following pictures... What happened in each of them?

As you can see, in both pictures we can find some people playing tug of war. What's the difference?
- In the top one, they apply the same force (300 Newtons) in opposite ways. Because the forces are balanced, no one is moving.
- In the bottom one, they apply different forces in opposite ways (the left team is pulling 100 Newtons more than the right team). Because the forces are unbalanced, the team on the right is moving onwards.
Let's practice a bit more identifying balanced and unbalanced forces!

GRAVITY AND WEIGHT
Gravity is a non-contact, pull force. All masses have gravity.
Is the force of gravity stronger on the Earth or on the moon? Why? Mass is the amount of matter in an object. It is measured in kilograms (kg). Weight is a force. It is mass x gravity. It is measured in newtons (N). Do you remember who discovered gravity over 300 years ago? You're right, Isaac Newton! Learn more about gravity and find very interesting activities related to it here: Gravity Pulls Things Down [Video, Discussion Questions, Vocabulary, Reading, Experiment and Quiz] Is the force of gravity stronger on the Earth or on the Moon? Why?
Remember that mass and weight aren't the same, are they?
UPTHRUST AND FLOATATION Upthrust is a contact, push force applied by water and air. It pushes objects in air and water up. The mass and volume of an object influence the amount of upthrust:
|
Archimedes, an Ancient Greek scientist, discovered upthrust in his bath over 2000 years ago!
En la serie de televisión Érase una vez… los inventores
∴ Experiment time! ∴ Do you want to check what Archimedes discovered? Watch the following videos and, if your parents let you, try them and tell us in class your results!
SIMPLE MACHINES We are almost done with this unit, guys! Now that we know a lot about matter and forces, let's talk about the instruments that make our life easier... You're right, machines! The first ones were simple machines with one or two parts. They used energy from people or animals to do work. Watch these videos to get to know more about them! Remember:
Some examples of lever are see-saws and scissors.
Some examples of pulley are wells and blinds.
Some examples of inclined plane are a slide and an emergency ramp.
Now it's your turn... can you think about more examples of simple machines around your city? If you find any of them, tell us in class! ∴ Experiment time! ∴ Do you want to feel like an authentic engineer? Watch the following videos and decide which simple machine you want to build!
REVISION MINDMAP. Will you be able to complete it with the missing words? PART 1
---
Have a look at the following presentation of unit 5 made using Prezi:
Now, have a look at the following links with videos and interesting facts:
Ficheros adicionales
UNIT 6.
THE IBERIAN PENINSULA IN ANCIENT HISTORY
 Wow, guys... Can you feel it? The end of the school year is in the air! We know you're doing a great effort, so let's finish it learning a bit more about history. T time, we will get to know more about Ancient Times in the Iberian Peninsula. Let's zoom in!
THE START OF ANCIENT HISTORY IN SPAIN First, let's refresh our minds... Do you remember which civilisations where living in the Iberian Peninsula at the end of Prehistory, during the Metal Ages?
You're right! The Celts and Iberians (Celtiberians). From about the 10th century B.C., people from three civilisations started to come to the Iberian Peninsula looking for metals. They also wanted to trade with the Celts and Iberians. They established colonies. Which were these three civilisations? Unscramble the letters to solve the mistery!
Watch the following videos to review what we have learnt about the three colonizers.
Finally, remember that thanks to Greeks, Phoenicians and Carthaginians, there were introduced:
Watch these videos about the Greeks, the Carthaginians and the Phoenicians HERE anD HERE Why did the Phoenicians, Carthaginians and Phoenicians come to the Iberian peninsula? Who established colonies in Cataluña, Andalucia, Murcia and the Balearic Islands? Can you find these autonomous communities in the map? Watch videos about the Romans: here and here. ColonisationPara saber más Ancient History on the Iberian Peninsula🍀🍀 🌱 🍀🍀
From 1100BC, Mediterranean cultures began arriving on the Iberian Peninsula and founding colonies. They were the Phoenicians, Ancients Greeks and Carthaginians.
What they all had in common was that their cultures were based on urban-living trade.
The Phoenicians:
The Ancient Greeks:
The Carthaginians:
¯\_(ツ)_/¯Watch these videos to learn more!
Do you think the Iberian Peninsula was crowded at that time? Well... another civilisation wanted to come: Rome! The Romans came from the Italian Peninsula. The Romans and Carthaginians were rivals. They both wanted to control the Mediterranean Sea. The Romans also fought different wars against the Celtiberians for almost 200 years. As you've seen, the Iberian Peninsula changed a lot during Ancient History... Let's have a look at these maps to review.
The Roman Empire on the Iberian Peninsula:
The Roma conquest of The Iberian Peninsula began in Emporio in 218 BC. It was a gradual conquest and finished the 19BC.
The Romans called the land Hispania.
Important figures and events:
Viriatus
Numantia was a Celtiberian town.
Roman Hispania:The Roman conquest ended in 19 B. C. This was when the Romans controlled all of the peninsula and called it Hispania. They divided Hispania into provinces and changed how the people of the Iberian Peninsula lived. Do you remember how these changes are called? That's it, Romanisation! Language: Latin. Many modern languages are based on Latin, they are called Romance Languages. Romance Languages: Spanish, French, Italian, Romanian... Religion: Emperor Constantine converted to Christianity in AD 312.
Seneca was born in Corduba (Córdoba) in 4 BC. He became tutor and advisor of Emperor Nero.
Trajan became emperor of Rome in AD 98. He constructed a column in The Roman Forum to celebrate his victory in Dacia (Romania).
Hadrian became emperor in AD 117. He built a stone wall to separate the Celtic tribes in Caledonia (Scotland) from the rest of Roman Britannia (Britain). Trajan and Hadrian Here you have some links to review aaaaaall the new things we have learnt: The Roman Conquest_Review activities [LiveWorksheets] Roman Hispania_Review activities [LiveWorksheets] The End of Roman Hispania and Fall of the Roman Empire_Review Activities [LiveWorksheets] Ancient History_ Quiz Show Review Game [Wordwall] Ancient History_Review Mindmap [LiveWorksheets]
REVISION MINDMAP. Will you be able to complete it with the missing words?
Ahora vamos a hacer un timeline. ¿ Te acuerdas cómo se hacía?
TE PUEDE AYUDAR A ESTUDIAR TARJETAS CON FECHAS Y DATOS
Have a look at the following presentation of unit 6 made using Prezi:
and at this set of activities to learn, play and review made with Quizlet: Last, but not least, here there are some videos and practice waiting for you:
Fill the gapsMatch the correct sentences.Roman Legacy
Match the Roman legacies.
Roman conquestRoman Citiziens form HispaniaAsterix and ObelixWATCH A VIDEO ABOUT ROME chistes Good bye and good luck
REPASO EN CASTELLANO
4º E. Primaria. Sociales EDITORIAL SANTILLANA EDITORIAL VICENS VIVES 11 4º E. Primaria. Naturales EDITORIAL SANTILLANA EDITORIAL VICENS VIVES |




















































































































![Matter and Forces [mindmap]_2.jpg](https://www.educa2.madrid.org/web/educamadrid/principal/files/4a0a6c8e-acaa-4b71-9e91-91328b9c3e59/Matter%20and%20Forces%20%5Bmindmap%5D_2.jpg?t=1619381805155&largeSize=true)


























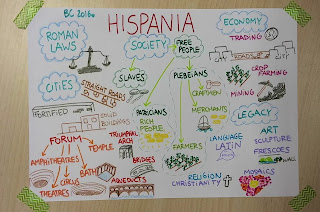






![Ancient Times [Mindmap].jpg](https://www.educa2.madrid.org/web/educamadrid/principal/files/91318a50-73bf-4ad1-a225-37417915df30/Ancient%20Times%20%5BMindmap%5D.jpg?t=1621969649946&largeSize=true)












No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario